Ansoff Matrix of Mission to Mars A
Posted by Matthew Harvey on Sep-01-2020
1. Introduction
The Ansoff matrix is a strategic tool developed to facilitate and guide businesses in decision pertaining to business growth. The Ansoff matrix offers four strategic choices to businesses to choose from – market penetration, market development, product development and diversification. An organization or a business is to choose any of these four strategies, or a combination – deepening on various internal and external factors.
The external factors may include aspects of political stability and economy of a region, and internal factors may include aspects of talent management, and resource capacities. Based on an analysis of the internal and external factors, organizations decide different strategies for growth – which may be broadly defined under the Ansoff matrix.
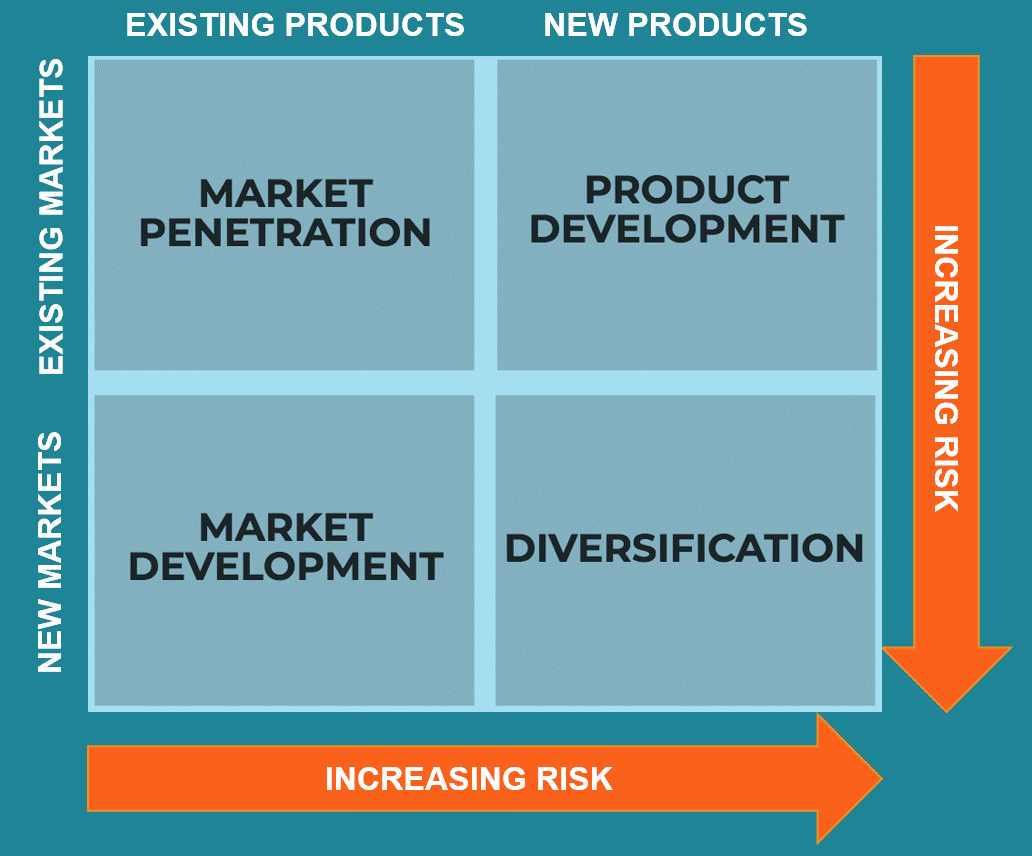
Figure 1 Ansoff Matrix (Daft, 2016)
1.1. The Mission to Mars A makes use of the Ansoff matrix for successful international growth
The Mission to Mars A has been successful in its global operations and business based on its strategic growth choices and decisions. These growth decisions and growth paths have been varied for different regions, at different time points – based on the internal and external organizational factors. However, the Mission to Mars A has successfully made use of the Ansoff matrix repeatedly to become one of the leading beverage giants internationally. Some of the strategies that Mission to Mars A has successfully used under the Ansoff matrix and categories are detailed below.
2. Market penetration
The market penetration strategy is used by businesses that seek growth for existing products in markets where their brands are existing, and already operational.
2.1. Increase production capacity
- Increased production capacity will allow Mission to Mars A to reach more customers within the same market
- Increased production capacity would also lead to more efficiency and effectiveness – especially for controlling overhead costs
- Controlled overhead costs would lead to competitive pricing and would appeal to the consumers in the same market
- Increased attractiveness and competitive pricing within the same market will lead to increased sales and consumption – and thus a higher market penetration
2.2. Increased marketing investment
- The Mission to Mars A can also increase its investment in marketing and advertising activities to increase market penetration
- The Mission to Mars A should try to develop and design engaging communication content that is relevant to its various market groups
- Engaging communication and investment in marketing activities, and advertising will allow the Mission to Mars A to reach more consumers within the same market
- With higher marketing investment, the Mission to Mars A will be able to increase its market penetration within the existing markets for existing products
2.3. Enhanced distribution
- The Mission to Mars A can explore new and innovative means of distribution
- The Mission to Mars A can also explore new channels of distribution for their products
- New and enhanced distribution channels and strategies will allow the Mission to Mars A to reach new consumer segments and consumer groups in the same market – which may have been inaccessible previously
- Improved supply chains and distribution systems may lead to increased penetration within the same market by improving accessibility
2.4. Competitive pricing
- The Mission to Mars A may introduce competitive pricing and price cuts to increase the appeal of its products
- Competitive pricing will be a source of competitive advantage for the company, and will lead to enhanced consumer engagement with the product
- At the same time, competitive pricing will increase the sales for the Mission to Mars A and lead to increased penetration
2.5. Reduce operational costs
- The Mission to Mars A can reduce operational costs to increase competitive pricing
- Competitive pricing will help the Mission to Mars A increase its sales volume and consumption
- Lower operational costs will lead to less costs being passed on to the consumers, and will make the products offered by the Mission to Mars A more desirable and affordable
- Higher affordability and accessibility will help the Mission to Mars A increase its market penetration
2.6. Acquiring competitors
- The Mission to Mars A can acquire competing players in the market
- The acquisitions will give the Mission to Mars A leverage in reaching different consumer groups and segments
- The acquisitions will also allow the Mission to Mars A to develop leverage through diversified supply chain and distribution channels
- Acquisitions will lead to higher penetration through improving the Mission to Mars A’s accessibility of different consumer groups and segments in existing markets
2.7. Partnerships and joint ventures
- The Mission to Mars A can also enter strategic p[partnerships and joint ventures with other players in the market
- These can be players belonging to similar industry, or even different industries
- Strategic partnerships and joint ventures will allow the Mission to Mars A to gain access to different consumer groups, and their market behaviour and consumption patterns
- Additionally, the Mission to Mars A will be mitigating risk factors through limited investment – which in turn will safeguard it against potential losses
- Joint ventures and partnerships can provide the Mission to Mars A with guided means of increasing penetration in existing markets
2.8. New product benefits and features
- The Mission to Mars A can identify new features and characteristics in existing products for existing markets
- This identification will lead to innovative and novice product consumption purposes and behaviour
- Consumers should also be made aware of these new and innovative usage patterns and consumptions ways of the Mission to Mars A products by the company
- Increased marketing and communication of new product use and benefits, along with characteristics and features will lead to increased consumption in existing consumer groups and segments, as well as in new consumer segments and groups
- This will facilitate the Mission to Mars A in improving its overall market penetration in existing companies
2.9. Increased frequency of consumption
- The Mission to Mars A can also initiate communication and marketing aimed at increasing the frequency of consumption of the products in existing markets
- Increased consumption frequency will lead to an overall increased consumption
- The Mission to Mars A will thus be able to increase the sales volume sold to existing consumers in existing markets
- The company will be able to increase its market penetration through these means
3. Market development
With market development strategies, the Mission to Mars A can enhance its business growth through introducing existing products in new markets. This will be possible for the Mission to Mars A with different strategies.
3.1. Research and development
- The Mission to Mars A should invest in research and development to identify possible new markets and consumer segments for its products
- The R&D should focus on identifying and understanding different market cultures, trends, and consumer behaviours - and how they differ dim consumer behaviour patterns in existing markets
3.2. Regional expansion
- The Mission to Mars A can expand regionally
- This will include expansion locally to different cities, or within the same geographic region
- Regional expansion should also take into consideration any cultural differences that will need to be accommodated in the expansion process in terms of marketing or product modifications and consumption methods.
3.3. International expansion
- The Mission to Mars A an also enjoy business growth through international expansion
- International expansion will allow Mission to Mars A to access different consumer groups, and increase its overall share of the pie
- International expansion will require the Mission to Mars A to conduct in-depth PESTLE, Porters 5 forces and SWOT analyses to develop a comparative strategy and overview for planned expansion
- The company will also need to understand the possible cultural differences, and make accommodations to its expansion strategy accordingly. Cultural differences should be taken into account in the process of global expansion.
3.4. New customer segments
- The Mission to Mars A can also explore new consumer segments in the same market for its products
- The company can identify new product uses and features and target new consumer segments for the existing products
- This will allow the company to tap into new markets and new market trends within the same market to help in growth and expansion
3.5. Brand awareness
- The Mission to Mars A also invests in activities of building brand awareness
- Building brand awareness is important to help the company reach new consumer segments, and increase visibility
- Increased brand awareness for the Mission to Mars A also leads to increased brand recall – which is important for purchase decisions
- Consequently, building brand awareness is important for increasing sales, and driving growth in new markets
3.6. Customer education
- The Mission to Mars A should also educate consumers in new markets for its products
- This market education is important for allowing consumers in understanding the products, and its offerings
- The consumers will also be able to understand consumption patterns for the products better with education
- The Mission to Mars A increases sales through educating new consumer segments in existing and new markets to lead to overall business development and growth/
4. Product development
When a company seeks to expand business growth in existing markets through new products, it is termed as product development. The Mission to Mars A drives product development in different ways.
4.1. Modifications to existing products
- The Mission to Mars A can introduce modifications and improvements in existing products to offer consumers new and enhanced offerings
- This will lead to increased sales and consumption of the product
4.2. Launch new products
- The Mission to Mars A also often engages in R&D activities to understand and identify new points of consumer demand
- The company then undergoes a NPD process, and develops and launches new products in the market for consumers
- This increases the breadth of the company’s reach, and also allows Mission to Mars A to penetrate new market segments
4.3. Research and development
- Mission to Mars A regularly invests in research and development – especially pertaining towards understanding market trends and consumer behaviour
- Investment in R&D has allowed the Mission to Mars A to remain competitive through innovation and creativity – in product launches as well as other functional areas such as marketing, operations and finances
- Research and development has also built the Mission to Mars A to become more efficient in its operations and routine activities.
4.4. Strategic partnerships
- The Mission to Mars A engages in strategic partnerships to explore options for product development as well
- Strategic partnerships allows Mission to Mars A to have access to new product developments, and processes with limited financial investment- and thus limited risk involved
- This is important for Mission to Mars A – to be able to understand the new product, and development process along with the market reaction and acceptability of the same before engaging in fill fledged production of own
4.5. Product quality
- The company can also engage in new product development through introducing different quality products in the same market
- This will allow the Mission to Mars A to penetrate new market and consumer segments, as well as target new consumer groups
5. Diversification
Diversification refers to business growth and development that occurs when a company engages in new product development in new markets. Diversification is an important and allows businesses like the Mission to Mars A to remain competent, innovative, and competitive – thereby remaining relevant for the consumer markets.
5.1. Vertical diversification
- Vertical diversification for the Mission to Mars A means looking for growth and business development by introducing new products under existing product lines.
- This means that the new product developments and launches by the Mission to Mars A would be similar to, and categorized under existing product groups and categories.
5.2. Horizontal diversification
- Horizontal diversification occurs when the Mission to Mars A decides to introduce and engage with new product developments and launches that are not associated with the existing products
- It is however beneficial to introduce new products launches and developments for products that share similar economic environments with the visiting products.
5.3. Diversification towards a new business
- The Mission to Mars A can also diversify into becoming a conglomerate by engaging in a different business altogether
- Diversification through a new business would involve the Mission to Mars A to explore new business ideas and option to launch or acquire for purposes of growth and development
5.3.1. Mergers and acquisitions
- One of the ways through which the Mission to Mars A may explore conglomeratic growth of entering new businesses is through mergers and acquisitions
- The Mission to Mars A can partner with, or acquire companies and businesses that interest it in an effort to diversify into new markets and new consume groups with products and services that are completely new, and not related to existing offerings
6. References
Ansoff, H., 1957. Strategies for diversification. Harvard business review, 35(5), pp. 113-124.
Chiu, Y., Chen , B., Shyu, J. & Tzeng, G., 2006. An evaluation model of new product launch strategy. Technovation, 26(11), pp. 1244-1252..
Cole, G., 2003. Strategic Management. Boston: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Daft, R., 2016. Contemporary Strategy Analyses. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Grant, R., 2010. Contemporary Strategy Analysis and Cases: Text and Cases. Hoboken: NJ: ohn Wiley & Sons.
Hill, C. & Jones, G., 2007. Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach. Boston: Cengage Learning.
Hrebiniak, L., 2005. Making strategy work. Philadelphia, PA: Wharton School Publishing.
Hussain, S., Khattak, J., Rizwan, A. & Latif, M., 2013. ANSOFF matrix, environment, and growth-an interactive triangle. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 2(2), pp. 196-206.
Kipley, D. & Lewis, A., 2011. Strategic Management: Incorporating Ansoff. New York: Pearson.
Martinet, A., 2010. Strategic planning, strategic management, strategic foresight: The seminal work of H. Igor Ansoff. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 77(9), pp. 1485-1487.
Moussetis, R., 2011. Ansoff revisited. Journal of Management History, Volume Jan.
Thompson, J. & Martin, F., 2010. Strategic Management: Awareness & Change. Hampshire: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Thomson, N., 2010. Basic Strategy in Context: European text and cases. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Witcher, B. J. & Chau, V. S., 2010. Strategic Management: Principles and Practice. Boston: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Warning! This article is only an example and cannot be used for research or reference purposes. If you need help with something similar, please submit your details here.
Related Articles
- Corporate Social Responsibility of Mission to Mars A
- Mission to Mars A 5C Marketing Analysis
- The vision statement of Mission to Mars A
- Organizational Culture of Mission to Mars A
- Mission to Mars A Generic and Intensive Growth Strategies
- Mission to Mars A Case Study Analysis & Solution
- Mission to Mars A Case Solution
- Blue Ocean Strategy of Mission to Mars A
- Hofstede Cultural Model of Mission to Mars A
- Porters Diamond Model of Mission to Mars A
- Mckinsey 7s Framework Of Mission to Mars A
- Resource Based View Of The Firm - Mission to Mars A
- VRIN/VRIO Analysis Of Mission to Mars A
- Net Present Value (NPV) Analysis of Mission to Mars A
- WACC for Mission to Mars A

Calib Noah
5.0

It was my first ever experience with this service. But it is beyond measure and I’m happy. Thank you for making my time bright...

Gaia Mike
5.0

I am a fan of writer #678281 who wrote the paper. Very good experience and I’m very happy. Recommended!

Robin Yanis
5.0

My paper was a very serious project and I couldn't bear a mistake in it. Hired this company and it provided a well-written paper to me. Grateful!

Lucy Smith
5.0

The paper expressed that the writer composed it with full deliberation without the mind to get the money. Thumbs up for this consideration!

Annie Micheal
5.0

This website is user friendly. Quick and easy process. The paper was delivered on time. I am delighted. Thanks a lot!

Falapa Blaise
5.0

I can only praise these guys because I obtained good scores. Thank you so much!
Next Articles
- 18376-Waterloo-Regional-Police-Services-Reassessing-the-CIMS-Project-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18377-Enterprise-Resource-Planning-Software--Ongoing-Maintenance-Cost-Benefit-Analysis-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18378-Bell-Atlantic-and-the-Union-City-Schools-A-The-Intelligent-Network-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18379-Solagen-Process-Improvement-in-the-Manufacture-of-Gelatin-at-Kodak-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18380-Waterloo-Regional-Police-Services-The-CIMS-Project-B-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18381-Singapore-TradeNet-A-Tale-of-One-City-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18382-Transformation-at-the-IRS-Chinese-Version-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18383-Lack-of-Coordination-in-Management-of-the-Three-Cross-Harbour-Tunnels-in-Hong-Kong-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18384-Venture-Law-Group-A-Ansoff-Matrix
- 18385-Atlanta-Symphony-Orchestra-Ansoff-Matrix
Previous Articles
- 1-Making-the-Case-Ansoff-Matrix
- 2-Joe-Smith-s-Closing-Analysis-B-Ansoff-Matrix
- 3-Joe-Smith-s-Closing-Analysis-A-Spanish-Version-Ansoff-Matrix
- 4-GMAC-The-Pipeline-Ansoff-Matrix
- 5-On-Writing-Teaching-Notes-Well-Ansoff-Matrix
- 6-Exxon-Corp-Trouble-at-Valdez-Ansoff-Matrix
- 7-Ashland-Oil-Inc-Trouble-at-Floreffe-A-Ansoff-Matrix
- 8-Ashland-Oil-Inc-Trouble-at-Floreffe-B-Ansoff-Matrix
- 9-Ashland-Oil-Inc-Trouble-at-Floreffe-C-Ansoff-Matrix
- 10-Ashland-Oil-Inc-Trouble-at-Floreffe-D-Ansoff-Matrix
Be a Great Writer or Hire a Greater One!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire Essay48 with BIG enough reputation.

Our Guarantees
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!







